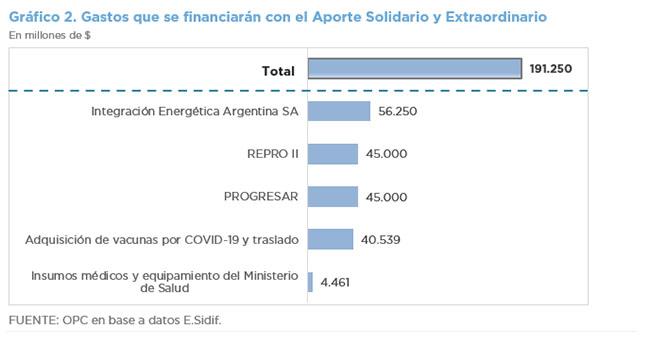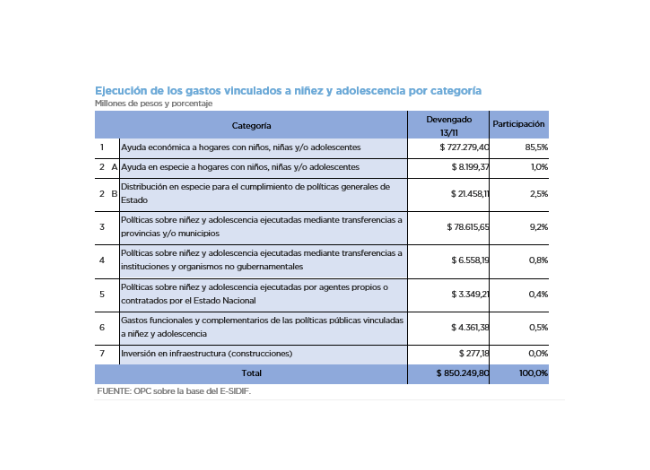
ANALYSIS OF NATIONAL TAX REVENUE – JUNE 2021
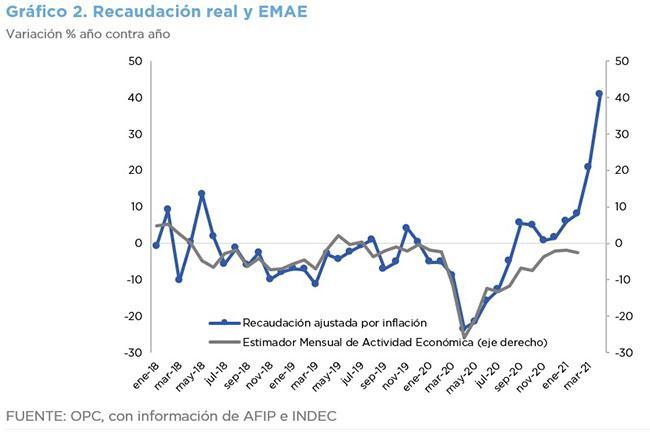
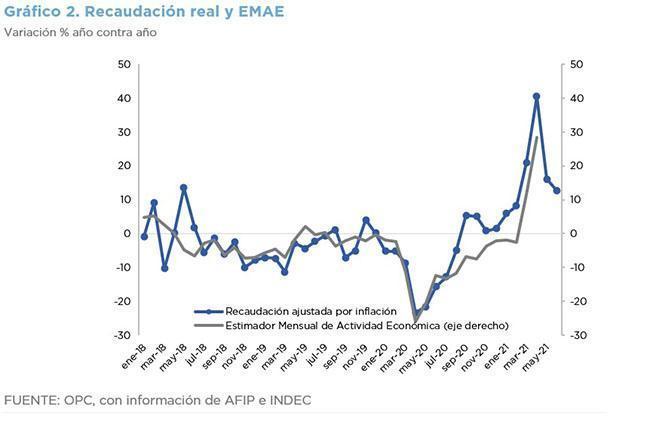
In June, tax revenues grew 69% year-on-year in nominal terms and 12.8% adjusted for inflation.
The increase was driven by the depreciation of the exchange rate (37% YoY), the increase in international commodity prices and regulatory changes. But the main factor behind the increase was the low basis of comparison since a year ago the Preventive and Compulsory Social Isolation (ASPO) was fully in force.
- Higher customs duties revenues (47.6% YoY) – due to the increase in the exchange rate and the recovery of imports – drove an improvement in VAT.
- The nominal increase of the dollar and the values of exported goods promoted an increase of 59.1% in the collection of Export Duties (YoY).
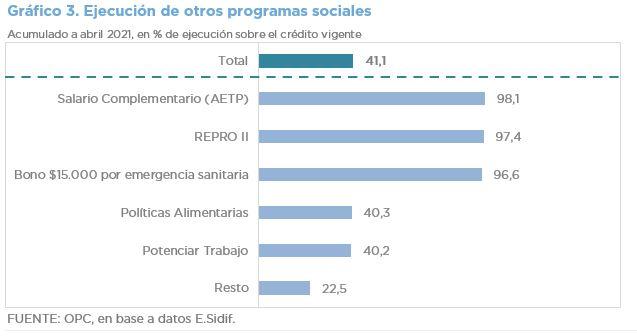
- Social Security resources increased for the third consecutive time in eight months, although the expansion of the wage bill has been systematically below the CPI since June 2018.
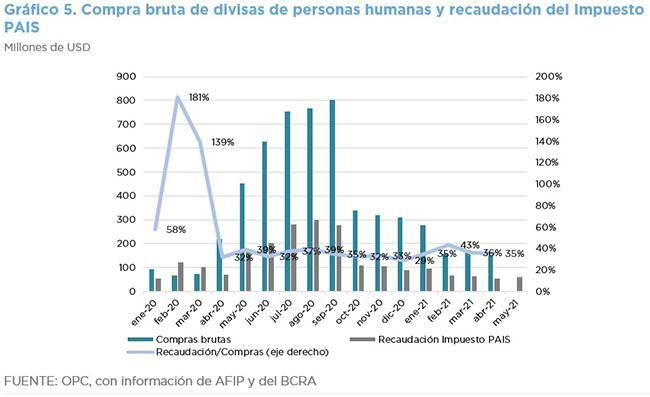
- PAIS Tax collection contracted again in the year-on-year comparison.
- The growth of the economy continues to be the main determinant of tax revenue, which fell steadily since mid-2018, due to a lower level of activity and the implementation of Law 27,430 on Tax Reform and began to recover after the worst effects of the measures adopted to contain the health effects of the pandemic.