ANALYSIS OF NATIONAL TAX REVENUE – MAY 2021
Partially because of the low basis of comparison, national tax revenue increased 72.7% in nominal terms and 14.3% in real terms as compared to the same month of the previous year.
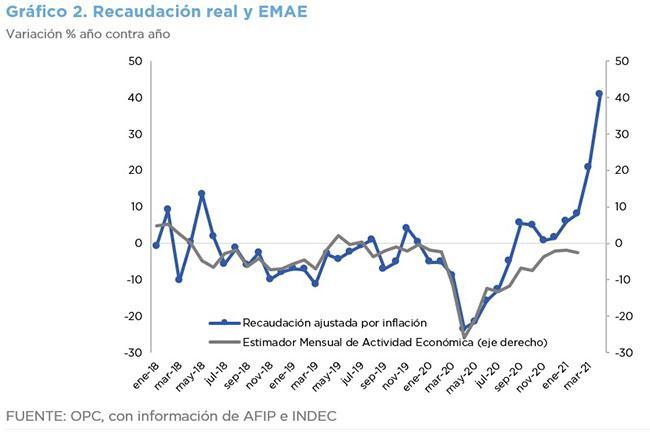
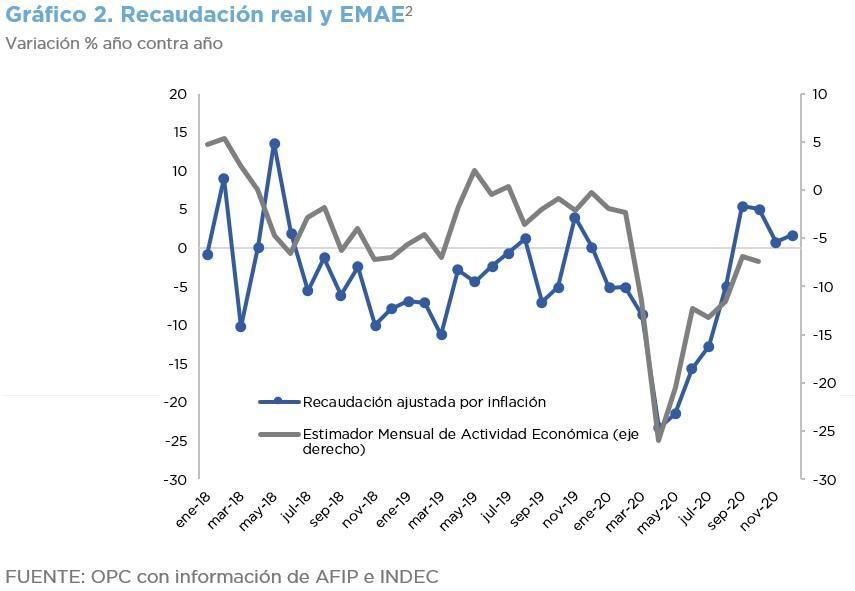
National Government revenues totaled AR$ 862.48 billion, which was the ninth consecutive month of increase (adjusted for inflation).
This behavior is partly explained by last year’s poor fiscal performance, when the mandatory isolation due to the health crisis was still in force, which lowers the basis for comparison.
The 39% nominal increase in the exchange rate also had an influence, which relatively improved the revenues from Export Duties and from the customs component of VAT, as well as from Income Tax. In addition, regulatory changes boosted the collection of shared taxes.
For taxes related to foreign trade, May 2020 also implied a low baseline, since the settlement of many transactions had been advanced to the end of 2019. An improvement in the international prices of exported goods also had an impact on the tax revenue increase.
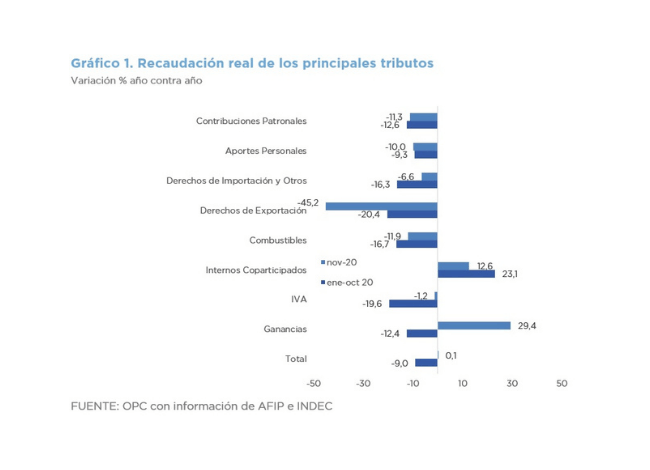
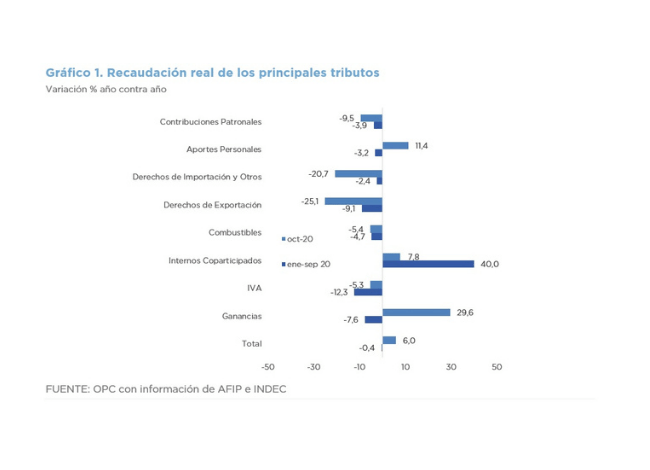
In absolute terms, the taxes that most contributed to the increase in revenue were VAT (accounting for 30% of the increase), Income Tax (20.2%), Export Duties (18.3%) and Social Security contributions (19.6%), which rose for the second time in eight months.
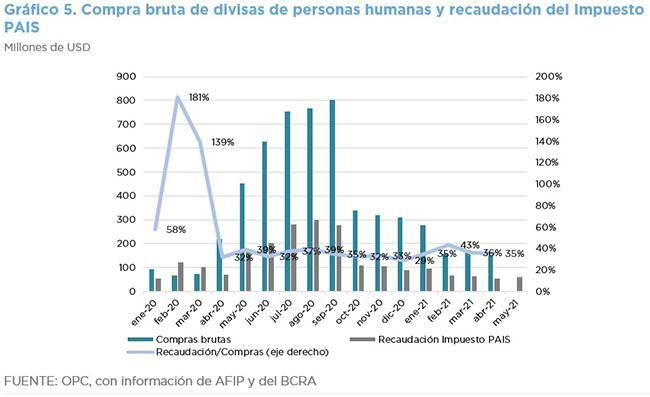
The PAIS Tax collected AR$ 5.49 billion in May, which represents a nominal reduction of 53.8%, because of the greater restrictions on the purchase of foreign currency.