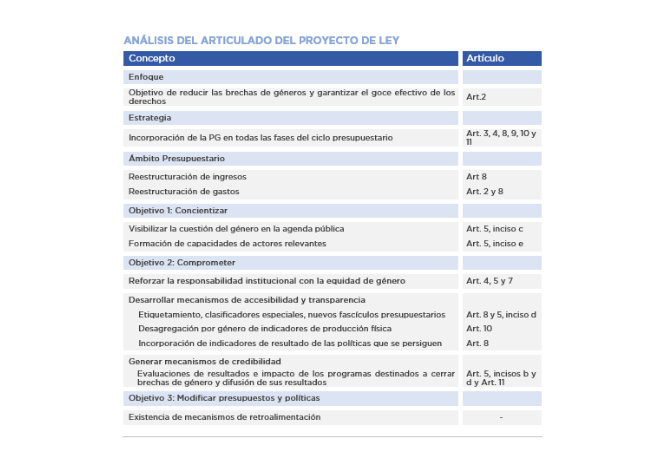
BUDGET EXECUTION OF GENDER – RESPONSIVE ACTIVITIES
This report analyzes the execution, as of November 13, of the budgetary activities labeled by the Executive Branch for their connection to gender equality.
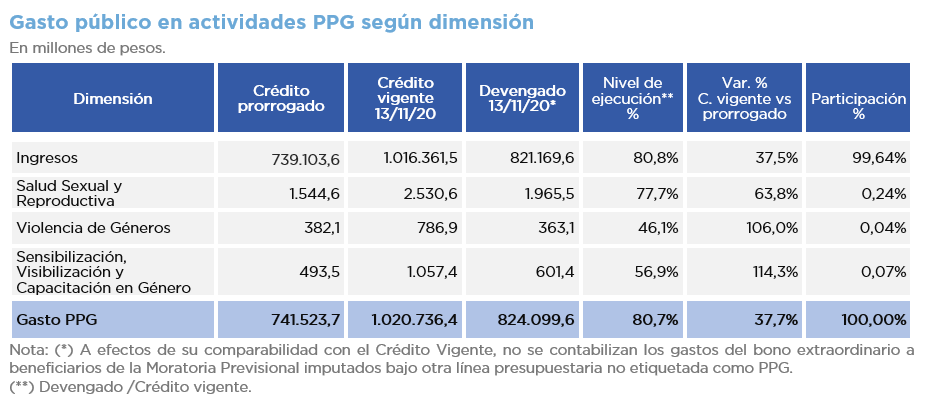
As of November 2020, the National Budget includes thirty-five (35) budgetary activities with a gender perspective. These activities accrued an expenditure of AR$832.2 billion as of November 13, 2020, which accounted for 14.6% of the total expenditure of the National Government.
Income policies (direct monetary transfers) amounted to approximately 99% of Gender-Responsive Budget (GRB) and ANSES, the agency in charge of managing and administering these policies, practically concentrated the entire GBR spending. The purpose of this social policy is to achieve financial independence for female beneficiaries.
- The level of physical execution of monetary transfers is very uneven. Some activities exceed 99% and others are barely above 26% of the annual schedule.
- There are new activities labeled in the 2021 Budget for the promotion of income.
- The budget for actions against gender-based violence was nominally doubled in relation to the extended 2019 appropriation, but the average level of execution is 46%.
- As of the third quarter of 2020, 124,468 victims of gender violence were assisted through the 144 hotlines.
- Out of the 55,000 doses for hormone treatments projected under the Gender Identity Law, 32,703 were distributed.