Progress in the preparation of a Gender Responsive Budget (GRB) in the country is focused on labeling budgetary activities with an impact on the gender gap from their design, without considering others that may also have that impact, although they have not been conceived for that purpose.
This report analyzes the implementation of activities with a gender perspective from January to August 2019: twenty-six budgetary actions that represent 3.7% of the public expenditure budgeted for the current fiscal year.
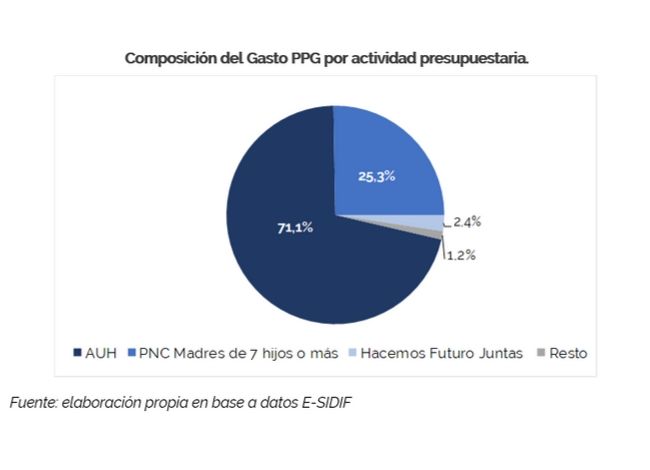
Expenditure is focused on initiatives that seek to strengthen the economic autonomy of women through direct monetary transfers and that privilege the mother status of the recipients. In fact, the Universal Child Allowance for Social Protection (AUH) represents more than 70% of GRB expenditure.
These activities show a lower level of implementation than total expenditure (56.5% compared to 62.9%) and great disparity among them.
The Gender Awareness, Visibility and Training dimension shows the highest level of execution (64.9%) as opposed to the Gender Violence and Sexual and Reproductive Health dimensions, whose accrued expenditure represented less than 10% for the first and little more than a third of the allocated appropriation for the second.