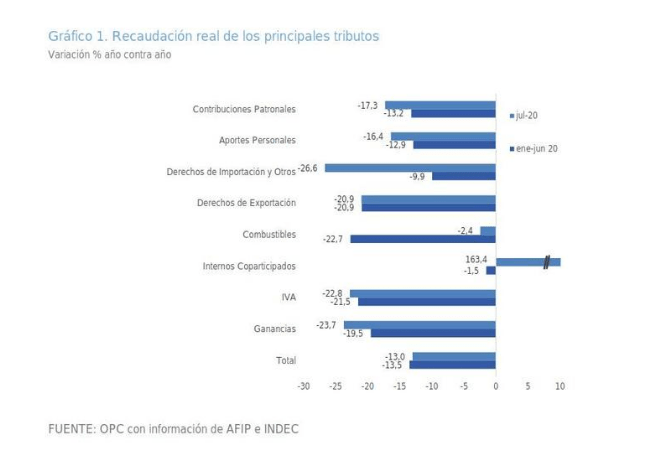
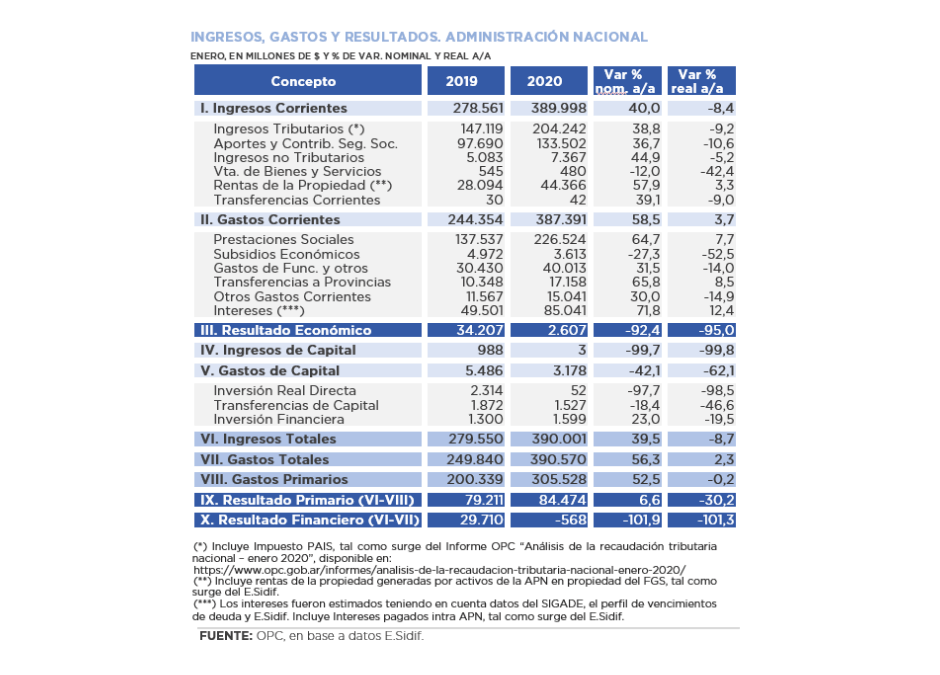
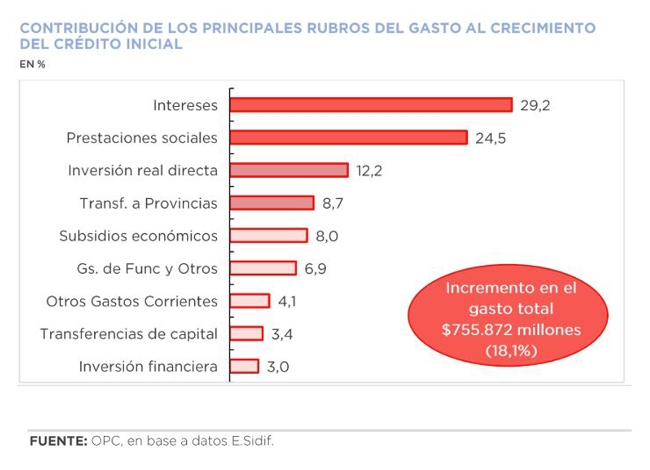
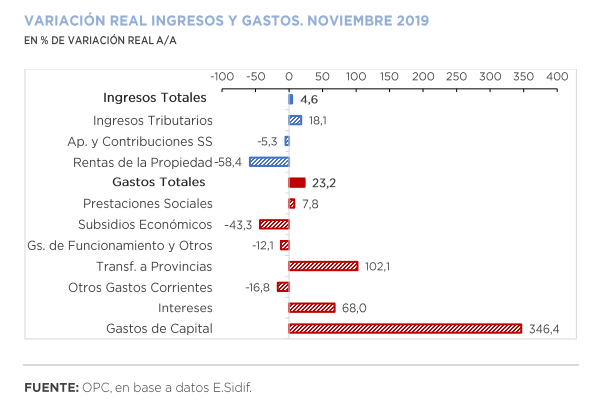
A review of the country’s fiscal federalism reveals the complexity of its parameters and the difficulties to establish a definitive consensus-based regime between the national government and the provinces, a constitutional mandate that has been pending for 23 years.
The federal tax co-participation regime was established by Law No.12,139 of 1935. The regulatory dispersion continued until the integration set forth in Law No.20,221 in force until 1984, recurrently infringed.
Among the decisions that infringed that law was the unilateral transfer of education and health functions to the provinces, without the respective financial allocations. This was the origin of the National Treasury contributions, an arbitrary mechanism to remedy problems as those caused by that discretionality. In 1980 pre-co-participations were introduced when it was decided that a portion of the VAT would be use for Social Security.
At the beginning of 1988, Law No.23,548 established a temporary distribution regime still in force. The secondary distribution scheme is not based on objective criteria and the original primary distribution, which reserved 54% to the provinces, was permanently altered.
The 1994 constitutional reform included co-participation in the National Constitution and provided for the enactment of a framework law before the end of 1996.
This mandate has not yet been accomplished and the most concrete legal approach was the series of fiscal pacts signed since 1992, whose interpretation and implementation led to legal disputes: federalism of concertation in our country lacks legal certainty.