IMPACT OF MOTHERHOOD ON WOMEN’S SALARIES AND PERMANENCE IN THE LABOR MARKET – IMPLICATIONS FOR THE ARGENTINE SOCIAL SECURITY SYSTEM
The role of women as household caregivers and, closely linked to this, motherhood, explain the unfavorable position in which women find themselves in the labor market and in access to social security benefits, which contributes to the origin and persistence of gender gaps.
Motherhood penalty in the Argentine labor market:
- The probability that a mother will enter the paid labor force is 11.5 percentage points lower than that of a woman without children, an effect that is more pronounced in the case of having children under 10 years of age.
- A woman with children earns 12% less than a woman who is not a mother, and this penalty is greater in the presence of adolescent children.
- These disadvantages are worsened by the number of children: a woman with three or more children is 15 percentage points less likely to work than a woman who is not a mother and has a relative wage 18% lower.
- The highest motherhood penalty is found among the youngest women, those with intermediate qualifications (with complete secondary education), and those in the informal labor market.
- This phenomenon worsens the gap and poverty of households and reinforces their reproduction. Thirty-one percent of Argentinean households are headed by a woman.
- Single mothers with children under the age of 18 earn the lowest hourly wages.
- Women up to the age of 29 earn as much as 42% less if they have three or more children.
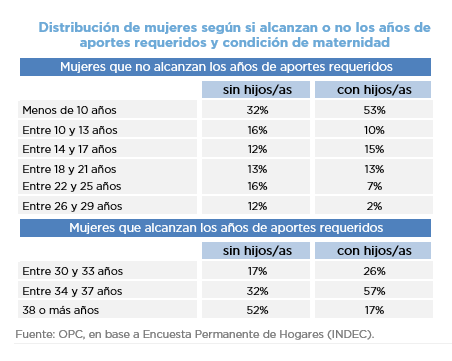
- Only 25% of mothers manage to reach the number of years of contributions required by the regulations, compared to 41% when considering women who do not have children.
- Within this select group, 9 out of 10 mothers and slightly more than 8 out of 10 women without children have completed university studies.
If structural issues that prevent reaching the required years of contributions are not addressed and the focus is placed only on access to pension benefits, the economic and financial consistency of the pension system could worsen. The formalization of labor would add resources to the public coffers, facilitating the self-financing of the pension system.