by Nicolas Perez | Dec 11, 2019 | Budget Execution
The primary balance for the month of November resulted in a deficit of AR$109.34 billion, the third month of the fiscal year with a negative outcome. Debt interest amounted to AR$124.23 billion, which had an impact on the deficit of AR$233.57 billion in the month and accumulated a disequilibrium of AR$568.49 billion in the eleven months of the current year. Even so, this figure implied a real improvement of 32.9% YoY compared to that recorded in November last year.
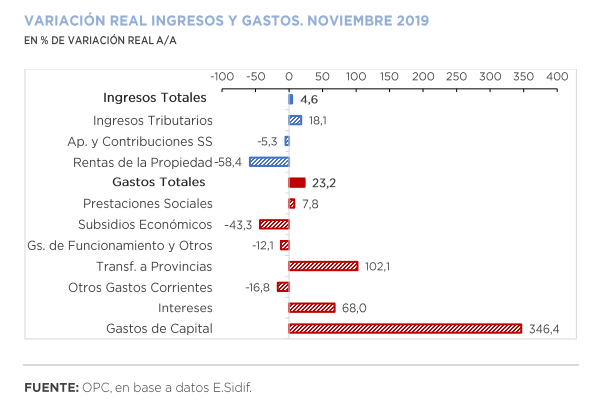
National government revenues increased 58.8% year-on-year (YoY), mainly explained by the growth of Export Duties (141.1% YoY in real terms), as the agro-export sector speeded up settlements due to the expectation of an increase in tax rates.
November was the month with the highest year-on-year expansion of total expenditures so far this year (87.2% YoY), mainly driven by the growth of real direct investment (1,302.6% YoY), transfers to provinces (206.9% YoY) and interest on debt (155.1% YoY).
As of November 30, 82.0% of total budget was accrued, with the execution of current transfers to the provinces (86.2%) standing out. During this period, the initial budget approved for the year increased by AR$797.26 billion, which represents 19.1% of the initial appropriation. A total of 88.8% of the amendments were implemented through Necessity and Emergency Decrees, and the remaining 11.2% through Administrative Decisions.
by Nicolas Perez | Aug 8, 2019 | Budget Execution
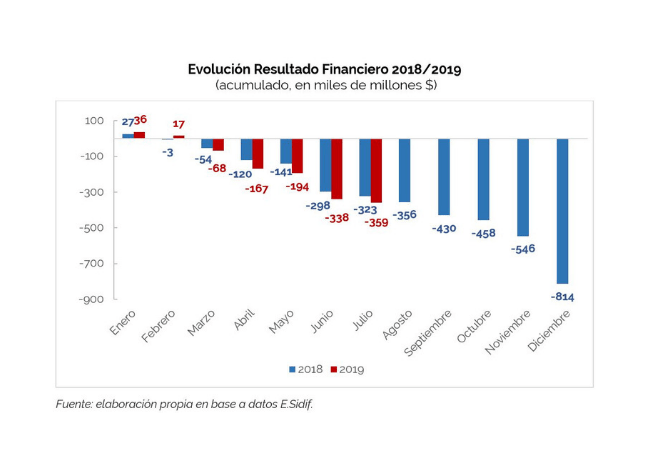
A surplus of AR$43.42 billion was recorded in July, a considerable improvement over the previous year’s figure (-AR$1.9 billion). The financial balance is negative by AR$21.04 billion but implies a drop of 44.4% in real terms in the year-on-year comparison. Transfers to provinces showed a monthly year-on-year drop for the first time this year.
- The increase in resources slowed down in July, although they grew again above expenditures (55.9% vs. 49.0%).
- Tax revenues (58.8%) led total revenue growth, while debt interest (186.4%) and capital expenditures (152.9%) were the fastest growing components of public expenditure.
- In the first seven months of the year, the financial balance was negative by AR$359.1 billion, an increase of 11.2% with respect to the same period of the previous year. In real terms, this represents a reduction of 27.9%.
- During the first seven months of the year, 57.0% of total expenditure was accrued, identical to the level recorded in the same period a year ago.
- From the beginning of the fiscal year to the end of July, the initial budget was increased by AR$88.3 billion, that is, 2.1%. The 39.2% of the amendments were implemented through the Necessity and Urgency Decree 193, while the remaining 60.8% were implemented through four Administrative Decisions.
by Nicolas Perez | Jul 31, 2019 | Budget Law
The Progress Report on the Draft Budget for 2020 estimated that 2019 will close with a 0.8% drop in the Gross Domestic Product and a stable primary balance, records that will improve next year.
For the following fiscal year, the government document predicts a strong increase of 3.5% of GDP and a primary surplus of 1%, although without specifying the expected variations in consumption, investment, and imports.
According to the government’s estimate, in both years there will be an increase in exports and the financial deficit will persist, but declining.
Inflation would be reduced to 26.1% by 2020, but the projection does not include values for the exchange rate or the interest rate.
Net public debt will fall in relation to GDP from 49.4% this year to 45.9% next year.
by Nicolas Perez | Jun 10, 2019 | Budget Execution
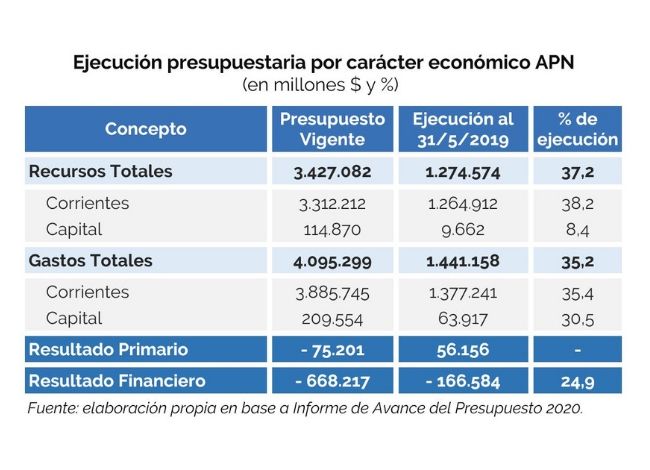
In May, the national government recorded a primary surplus of AR$23.99 billion but a financial deficit of AR$22.38 billion, within a framework of an acceleration in the fall of revenues in real terms. Expenditures, also in contraction, had the seventh month of decline measured against inflation.
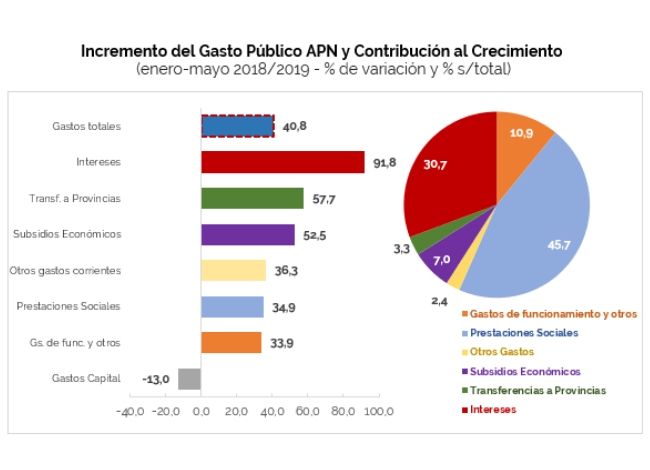
In the term January-May, expenditures increased 40.8% year-on-year. Interest on debt, transfers to provinces and economic subsidies recorded the largest expansions in the period with 91.8%, 57.7% and 52.5% YoY, respectively. Social benefits (34.9% YoY), operating expenses (33.9% YoY) and capital expenditures (-13.0% YoY) were below the increase in total expenditure.
Social benefits account for 45.7% of the increase in total expenditure, while interest payments account for 30.7%. Both explain 76.4% of the increase in expenditure in the period under analysis.
- National government revenues (40.5% YoY) again grew above expenditures (36.9% YoY), although the differential is reduced to 3.6 percentage points (p.p.) (5.2 p.p. in April).
- Personnel expenditure recorded a real fall of 14.6% YoY, in line with the retraction experienced in the salaries of several sectors (SINEP).
- After the first five months of the year, the financial balance is in deficit by AR$180.51 billion, reflecting a real reduction of 17.0% compared to the same period of the previous year.
- So far this year, the expenditure components that grew the most were Debt Interest (91.8% YoY), Transfers to Provinces (57.7% YoY) and Economic Subsidies (52.5% YoY). At the other extreme, capital expenditure contracted 13.0% YoY in nominal terms.
- The 76.3% of national government expenditure is rigid.
- At the end of May, the execution level of total expenditure reached 35.4% with respect to the current appropriation, higher than the level observed during the same period of the previous year, which reached 32.3%.
by Nicolas Perez | Jun 7, 2019 | Tax Revenue
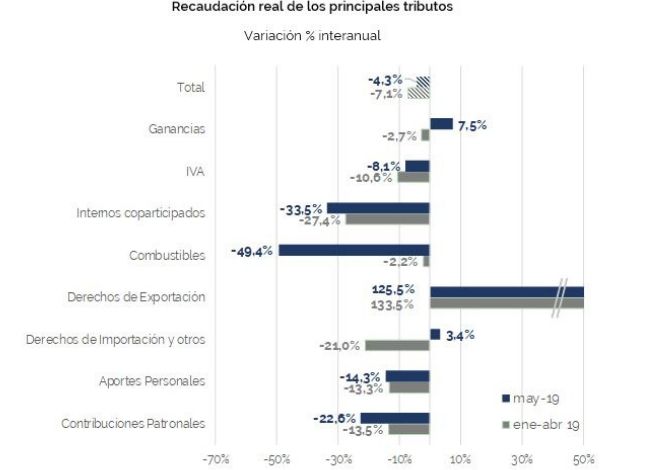
In May, tax revenue grew 50.4% in nominal terms with respect to the same month of the previous year but declined 4.3% in real terms during the same period. This decline deepens to 6.5% when considering the first five months of the year.
Overall tax revenue has been declining in real terms for eleven consecutive months, although it began to reduce the rate of decline.
In this context, Income Tax exceeded the collection expectations for the month with an increase of 7.5% year-on-year in real terms. Together with taxes on foreign trade, it is one of the taxes whose growth exceeded inflation.
VAT contracted by 8.1% in May, although this record implies a deceleration of the falls of the last seven months.
The decline in Social Security resources deepened because of the deterioration of the labor market and the changes in the employer contributions system. However, in the fifth month of the year, Social Security resources might have found its lowest level, and in the following months the trend may consolidate.
by Nicolas Perez | Apr 11, 2019 | Tax Revenue
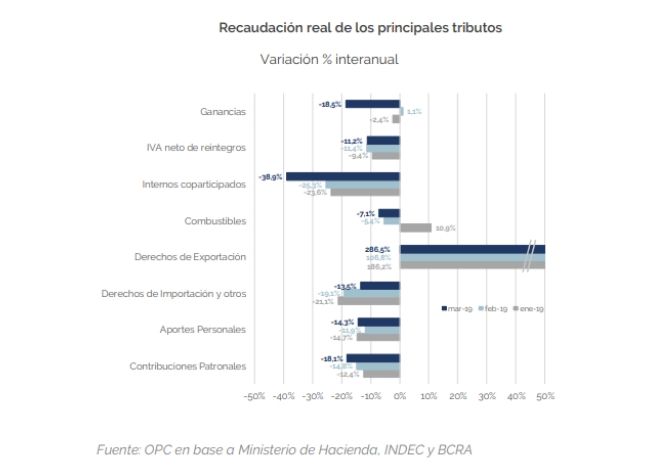
In the third month of the year, national public sector revenues grew by 37.3% in nominal terms compared to the same period of the previous year but fell by 10.5% in real terms. Similar behavior was observed in the first quarter of the year.
This performance also entails a decline compared to previous months and reaffirms that government revenues are strongly linked to the level of economic activity, as shown by the VAT DGI, which fell 7.3%.
Income Tax contracted by 18.5%, partly due to the deferral of some maturities. The significant growth in Export Duties allowed mitigating the fall in the most important taxes of the national tax structure (VAT, Income Tax and Social Security Contributions).






